World Health Organization warns that there are more than 30 different viruses, bacteria and parasites that are transmitted through sex and that more than 1 million STIs are acquired every day worldwide without people noticing.
In 2020, WHO revealed that there are 374 million new infections whereby chlamydia infection led by 129 million, gonorrhea (82 million), syphilis (7.1 million) and trichomoniasis (156 million).
In the recent research we found out that Syphilis is among the deadliest and easily transmitted STI infecting millions of people everyday globally.
It is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum which progresses through four stages:
Early, secondary, latent, and tertiary. The VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) test screens for syphilis by detecting antibodies produced in response to the infection.
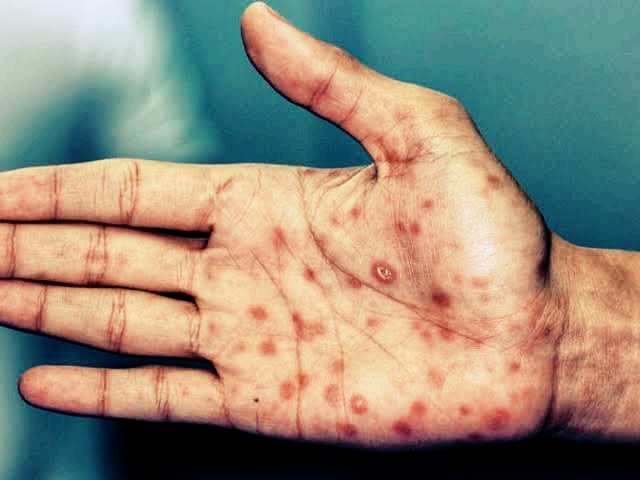
Signs and Symptoms of Syphilis
The symptoms for Syphilis vary by stage:
Primary: Characterized by painless sores (chancres) where the bacteria entered.
Secondary: Includes body rash, sore throat, hair loss, muscle aches, and other systemic symptoms.
Latent: Can be asymptomatic but still infectious.
Tertiary: If untreated, can lead to severe complications affecting organs like the brain, nerves, eyes, and heart, potentially leading to death.
Major Diagnosis and Testing
A positive VDRL test indicates the presence of syphilis infection. Testing is crucial as early diagnosis allows for effective treatment with penicillin, which can cure syphilis at all stages.
Transmission and Prevention
Syphilis is highly contagious through sexual contact and can also be transmitted from mother to baby during pregnancy or childbirth. Using protection like condoms can reduce the risk of transmission.
Treatment and Prognosis
Early-stage syphilis is curable with antibiotics, but untreated syphilis can cause irreversible damage and even be fatal. Regular testing and prompt treatment are essential for managing and preventing complications.
Read: Your Questions and Answers:
What are the symptoms of syphilis in a woman?
These syphilis symptoms may come and go for up to 2 years. They include body rashes that last 2 – 6 weeks — often on the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet. There are lots of other symptoms, including mild fever, fatigue, sore throat, hair loss, weight loss, swollen glands, headache, and muscle pains.
How long does VDRL stay positive?
VDRL test titers should decline at least 4-fold within 3–6 months after therapy for primary or secondary syphilis, and within 12–24 months for latent syphilis. IgM ELISA might be a supplement for diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
What happen if VDRL is reactive?
A reactive CSF-VDRL test, free of blood or other contaminants, usually indicates past or present syphilis infection of the central nervous system (CNS). A BFP test result is rare in spinal fluid. A nonreactive VDRL test may indicate that the patient does not have neurosyphili2
Can a girl give a guy syphilis?
You can catch syphilis by having unprotected oral, vaginal or anal sex with anyone who is in the first 2 stages of the infection. Syphilis is highly contagious when the sore or rash is present. Pregnant women who have syphilis can pass on the infection to their baby during pregnancy or birth
Can sperm transmit syphilis?
Unfortunately the syphilis will stay without treatment and will continue to be spread through semen. Syphilis is spread through oral sex as well as anal sex, or deep kissing/rubbing and grinding if coming in contact with a syphilis sore or if semen is present.
How can you tell if a man has syphilis?
You might notice that the lymph nodes near your groin are enlarged. Typically, the first visible sign of syphilis is a small, painless sore (doctors call it a “chancre”) on the skin (you may develop several sores). It normally appears at the spot where the bacteria entered your body.
Should I be worried if I test positive for syphilis?
If it’s not treated and develops to a late stage, it can cause permanent damage to your health. Treatment can still help, but it will not reverse the damage. In rare cases, untreated syphilis can even cause death. Syphilis tests can help diagnose the infection in the early stages, when it’s easiest to cure.
How long does it take to cure syphilis?
One shot of penicillin. Late stage: Three shots of penicillin, with one shot given each week for three weeks. Syphilis affects your nervous system: Penicillin given through an IV (intravenous) infusion, with treatment given once a week for two weeks.
Can syphilis be cured permanently?
Syphilis is simple to cure when it’s found and treated in its early stages. The preferred treatment at all stages is penicillin. This antibiotic medicine can kill the bacteria that causes syphilis. If you’re allergic to penicillin, your health care team may suggest another antibiotic.
Remember that getting tested regularly, especially if sexually active, helps in early detection and treatment of syphilis, ensuring better health outcomes and preventing transmission to others.



