
Did you know that a woman may never experience pregnancy after unprotected sex for an approximate period of 10 years? With the current birth control contraceptives family planning has even become more easier.
In this comprehensive guide you will find the best woman birth control contraceptives being used nowadays.

Intrauterine devices (IUDs) have become increasingly popular as a reliable form of birth control for women worldwide.
These small, T-shaped devices are inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider and offer a high level of effectiveness in preventing pregnancy.
Here, we delve into the various aspects of IUDs, from their definition and types to their safety and potential side effects.
What is an IUD?
An intrauterine device, commonly known as an IUD, is a small contraceptive device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
It is one of the most effective forms of birth control available, with a success rate of over 99%.
Once in place, an IUD provides continuous protection without requiring daily attention, making it a convenient option for many women.
Types of IUDs
There are two main types of IUDs: hormonal and non-hormonal.
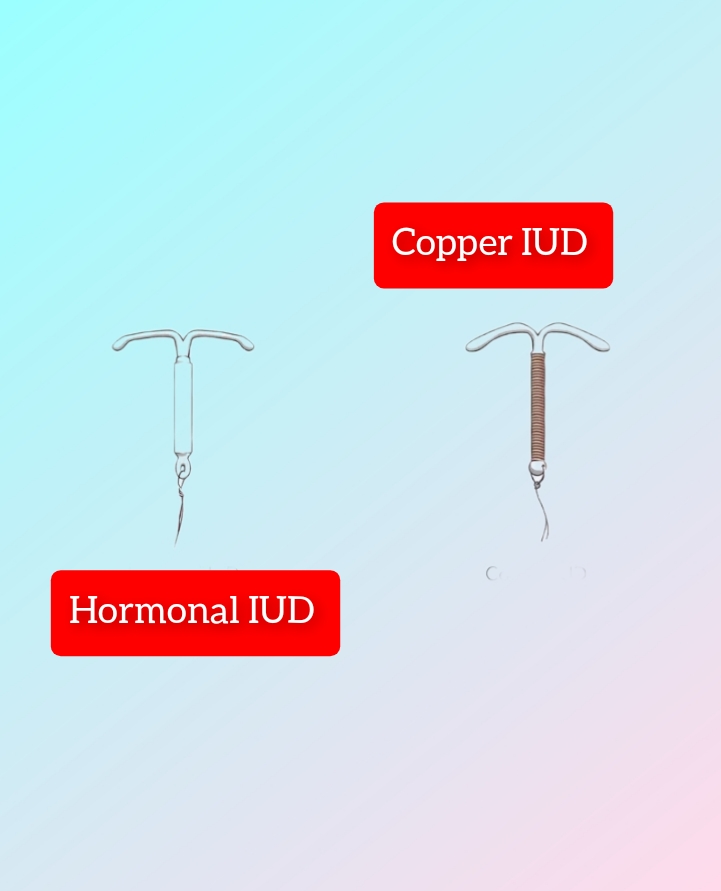
1. Hormonal IUDs
These devices release a small amount of progestin, a synthetic hormone similar to progesterone, into the uterus.
This hormone thickens cervical mucus, which makes it difficult for sperm to reach and fertilize an egg.
Hormonal IUDs can also prevent ovulation in some cases. Popular brands include Mirena, Skyla, Liletta, and Kyleena.
2. Non-Hormonal IUDs
Also known as copper IUDs, these devices do not contain hormones. Instead, they are wrapped in copper, which creates an environment in the uterus that is toxic to sperm, preventing fertilization.
Non-hormonal IUDs are effective immediately after insertion and can remain in place for up to 10-12 years, depending on the brand. Examples include ParaGard.
Effectiveness of IUDs
Research consistently demonstrates that IUDs are highly effective at preventing pregnancy. With a success rate of 99% or higher, IUDs are comparable to sterilization in terms of their contraceptive efficacy.
Their effectiveness is not dependent on user compliance, unlike birth control pills or condoms, which may be less reliable if not used correctly or consistently.
Side Effects of IUDs
While generally safe and well-tolerated by most women, IUDs may cause some side effects, which can vary depending on the type of device:
1. Hormonal IUDs
Common side effects may include irregular bleeding or spotting, especially during the first few months after insertion.
Some women may experience headaches, breast tenderness, or mood changes. In rare cases, hormonal IUDs can lead to more serious complications such as infection or perforation of the uterus.
2. Non-Hormonal IUDs
Copper IUDs may cause heavier menstrual bleeding and more painful cramps in some women. These symptoms often improve over time but can be managed with medical intervention if necessary.
Like hormonal IUDs, there is a small risk of uterine perforation or infection with non-hormonal devices.
Intrauterine devices are a highly effective and convenient option for birth control, offering long-term protection with minimal maintenance.
Whether opting for a hormonal or non-hormonal IUD, women should discuss their options with a healthcare provider to determine the best choice based on their individual health needs and preferences.
While IUDs are generally safe, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and seek medical advice if any concerns arise.
By understanding the benefits and considerations of IUDs, women can make informed decisions about their reproductive health and contraceptive choices.
